ArgoCD Autopilot: The Opinionated Path to True GitOps [under development]
Few days ago I came across a great ArgoCon talk from Dustin Van Buskirk (Codefresh). Dustin presented ArgoCD Autopilot: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hIcKOJhnZPg&t
The concept sounded so promising that I had to give it a go on my new home lab.
NOTE: Argocd Autopilot is under development thus it is not Prod Ready. So far, only Raw YAML and Kustomize are supported. This beeing said, it won’t work if you try bootstraping an application from a Repo where Helm Charts are located (supporting Helm is part of the Roadmap). I tried…It failed. Nonetheless, I keep folowing up the project closely.
This initial friction can slow down adoption and introduce inconsistencies.
1. The Core Philosophy: GitOps All the Way Down
Before we get started, here are the Requirements:
- Familiar with ArgoCD
- Installed kubectl command-line tool
- Have a kubeconfig file (default location is
~/.kube/config) - Installed git command-line tool
- Installed argocd-autopilot CLI: https://argocd-autopilot.readthedocs.io/en/stable/Installation-Guide/
- Create an Argocd Autopilot Git Repo (empty)
- export GIT_REPO=https://github.com/owner/name
- Git Token (PAT) – Select Scopes (repo):
- export GIT_TOKEN=ghp_PcZ…IP0
The bootstrap command pushes the necessary manifests to your designated GitOps repository, creating an autopilot-bootstrap application that manages the argo-cd application. This ensures that even ArgoCD’s configuration is version-controlled and auditable.
root@YodaLinux:~# argocd-autopilot repo bootstrap
INFO cloning repo: http://192.168.0.44:88/antho-group/argo-autopilot.git
Enumerating objects: 3, done.
Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done.
Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 (from 0)
INFO using revision: "", installation path: ""
INFO using context: "default", namespace: "argocd"
INFO applying bootstrap manifests to cluster...
namespace/argocd created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/applications.argoproj.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/applicationsets.argoproj.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/appprojects.argoproj.io created
serviceaccount/argocd-application-controller created
serviceaccount/argocd-applicationset-controller created
serviceaccount/argocd-dex-server created
serviceaccount/argocd-notifications-controller created
serviceaccount/argocd-redis created
serviceaccount/argocd-repo-server created
serviceaccount/argocd-server created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-application-controller created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-applicationset-controller created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-dex-server created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-notifications-controller created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-redis created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-server created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-application-controller created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-applicationset-controller created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-server created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-application-controller created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-applicationset-controller created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-dex-server created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-notifications-controller created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-redis created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-server created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-application-controller created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-applicationset-controller created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/argocd-server created
configmap/argocd-cm created
configmap/argocd-cmd-params-cm created
configmap/argocd-gpg-keys-cm created
configmap/argocd-notifications-cm created
configmap/argocd-rbac-cm created
configmap/argocd-ssh-known-hosts-cm created
configmap/argocd-tls-certs-cm created
secret/argocd-notifications-secret created
secret/argocd-secret created
service/argocd-applicationset-controller created
service/argocd-dex-server created
service/argocd-metrics created
service/argocd-notifications-controller-metrics created
service/argocd-redis created
service/argocd-repo-server created
service/argocd-server created
service/argocd-server-metrics created
deployment.apps/argocd-applicationset-controller created
deployment.apps/argocd-dex-server created
deployment.apps/argocd-notifications-controller created
deployment.apps/argocd-redis created
deployment.apps/argocd-repo-server created
deployment.apps/argocd-server created
statefulset.apps/argocd-application-controller created
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/argocd-application-controller-network-policy created
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/argocd-applicationset-controller-network-policy created
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/argocd-dex-server-network-policy created
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/argocd-notifications-controller-network-policy created
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/argocd-redis-network-policy created
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/argocd-repo-server-network-policy created
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/argocd-server-network-policy created
secret/argocd-repo-creds created
INFO pushing bootstrap manifests to repo
INFO applying argo-cd bootstrap application
I1207 00:53:33.192347 190451 warnings.go:110] "Warning: metadata.finalizers: \"resources-finalizer.argocd.argoproj.io\": prefer a domain-qualified finalizer name including a path (/) to avoid accidental conflicts with other finalizer writers"
application.argoproj.io/autopilot-bootstrap created
INFO running argocd login to initialize argocd config
E1207 00:53:33.226056 190451 portforward.go:391] "Unhandled Error" err="error copying from remote stream to local connection: readfrom tcp4 127.0.0.1:41009->127.0.0.1:50226: write tcp4 127.0.0.1:41009->127.0.0.1:50226: write: broken pipe" logger="UnhandledError"
'admin:login' logged in successfully
E1207 00:53:33.839390 190451 portforward.go:391] "Unhandled Error" err="error copying from remote stream to local connection: readfrom tcp4 127.0.0.1:41009->127.0.0.1:50242: write tcp4 127.0.0.1:41009->127.0.0.1:50242: write: broken pipe" logger="UnhandledError"
Context 'autopilot' updated
INFO argocd initialized. password: xxxxxxxxxxxxx
INFO run:
kubectl port-forward -n argocd svc/argocd-server 8080:80
NOTE: INFO output
- ArgoCD bootstrap manifest got pushed to our GitLab repo (bootstrap/ subfolder)
- ArgoCD application gets created in Argocd (we can now see ArgoCD components via the ArgoCD GUI)
- You can recover the argocd “admin” user password
- The installer sugested to port-forward the ArgoCD GUI, however I prefered to patch the argocd-server into a NodePort (OK for testing).
kubectl patch svc argocd-server -n argocd -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort"}}'
(base) root@YodaLinux:~# kubectl get svc -n argocd | grep argocd-server
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
argocd-server NodePort 10.43.22.239 <none> 80:32466/TCP,443:30783/TCP 6m6s
I can now access ArgoCD GUI via my-server-ip:32466
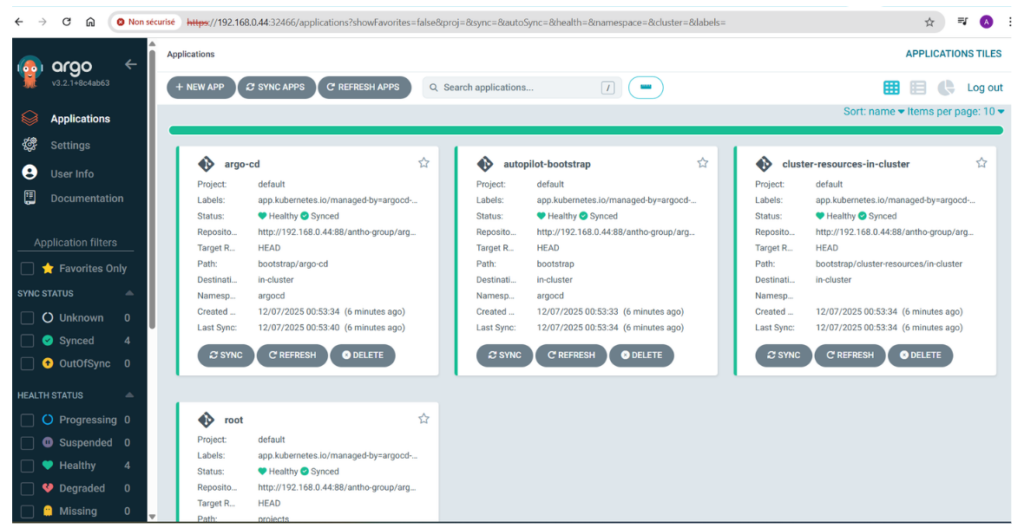
Now lets create an ArgoCD project:
(base) root@YodaLinux:~# argocd-autopilot project create production
INFO cloning git repository: http://192.168.0.44:88/antho-group/argo-autopilot.git
Enumerating objects: 18, done.
Counting objects: 100% (18/18), done.
Compressing objects: 100% (15/15), done.
Total 18 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 (from 0)
INFO using revision: "", installation path: "/"
INFO pushing new project manifest to repo
INFO project created: 'production'
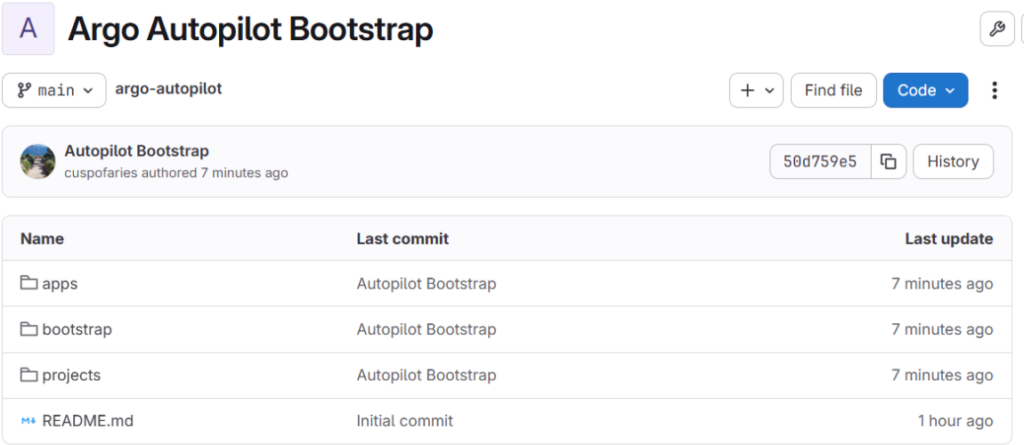
On my GitLab Repo I can now see that /bootstrap and /projects subfolders got updated with ArgoCD YAML manifests (ArgoCD Autopilot pushed manifests to my GitLab Repo).
Now what is going on with the /apps subfolder ?
This folder will get filled with ArgoCD YAML manifest once you installed your applications via the Argocd-autopilot command. Argocd-autopilot will be able to install applications located in their own GitLab repo as long it is Raw YAML or Kustomize format. We are going to see this in the second part below.
2. Streamlined Application Deployment with ApplicationSets
Once bootstrapped, adding new applications is where Autopilot truly shines. Instead of manually writing complex Application or ApplicationSet YAMLs, you use a simple CLI command:
argocd-autopilot app create my-app --app <repo-url> --project production3. The Ultimate Benefit: Disaster Recovery as a Single Command
argocd-autopilot repo bootstrap --recover
